We have a broad portfolio of programs
in clinical and research stages
-
01.About the Drug Candidate
SKI-G-801 is a new, synthetic, low-molecular-weight drug candidate that treats acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by selectively inhibiting FLT3. FLT3 is a kinase that is closely associated with the pathogenesis of AML and drug resistance.
Several mutations within the FLT3 gene that activate its kinase activity have been identified as one of the factors causing AML. These mutations are known to keep FLT3 kinase activated at all times independent of the FLT3 ligand, causing overproliferation of hematopoietic stem cells and preventing their normal differentiation. In all AML patients, FLT3-related mutations are found at a frequency of up to 35%. Point mutations in the FLT3-ITD (Internal tandem duplication) and FLT3-TKD (Tyrosine kinase domain) are two representative forms of FLT3 mutations, which account for 25-30% and 7-10%, respectively, of all AML patients.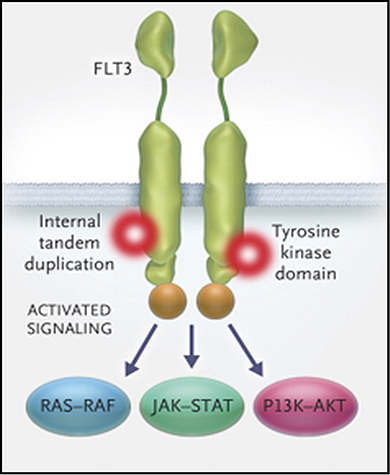 Role of FLT3 in Hematopoietic stem cells of an AML patient
Role of FLT3 in Hematopoietic stem cells of an AML patient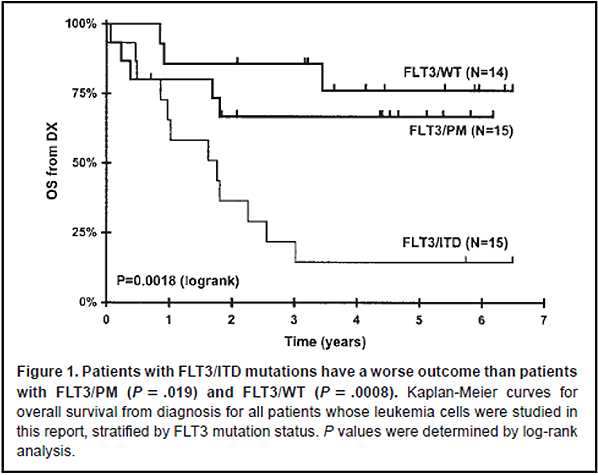 Impact of FLT3 mutation on the survival of AML patients
Impact of FLT3 mutation on the survival of AML patientsSource : Brown O. et al., Blood 104:1841-1849, 2004
SKI-G-801 has excellent selectivity for FLT3, shows very strong inhibitory activity not only against the wild-type FLT3, but also against mutant kinases, including FLT3-ITD and FLT3-D835Y (TKD mutation), and maintains the FLT3 inhibitory activity even in an environment of high ATP concentrations. As such, SKI-G-801 shows persistent FLT3 inhibitory effect in vivo.
SKI-G-801 is a best-in-class new drug candidate with a potential to solve key issues that appear in other competitors’ drugs, which have been approved or are currently under development. Such issues include short duration of inhibitory effect, drug resistance, poor inhibition of FLT3 mutations, decreased efficacy in plasma, and loss of efficacy in bone marrow.
-
02.Current Progress
SKI-G-801 is undergoing phase 1 clinical trial for treatment of AML
-
03.Clinical Trial Information
-
View more
Study to Find a Safe and Effective Dose of SKI-G-801 in the Treatment of Patients With Acute
Myeloid Leukemia (AML) (February 2018)
-
-
04.About the Disease
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a disease that occurs when hematopoietic stem cells act abnormally, suppressing the normal differentiation and function of related blood cells.
It is an acute disease in which each tissue is infiltrated and severe immune dysfunction and easy or excessive bleeding (systemic condition prone to bleeding) appear due to the paralysis of normal bone marrow function. If not treated, the patient will die within several months.
Although the exact cause of this disease is unknown, factors, such as smoking, genetic predisposition, irradiation, chemical and other occupational exposures, and anti-cancer chemotherapy drugs, are believed to cause changes in the cancer gene or the genes in the adjacent region, as a result of which the cancer gene is activated, causing AML. Treatment includes anti-cancer chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.