We have a broad portfolio of programs
in clinical and research stages
ROCK2 inhibitor
-
01.About the Drug Candidate
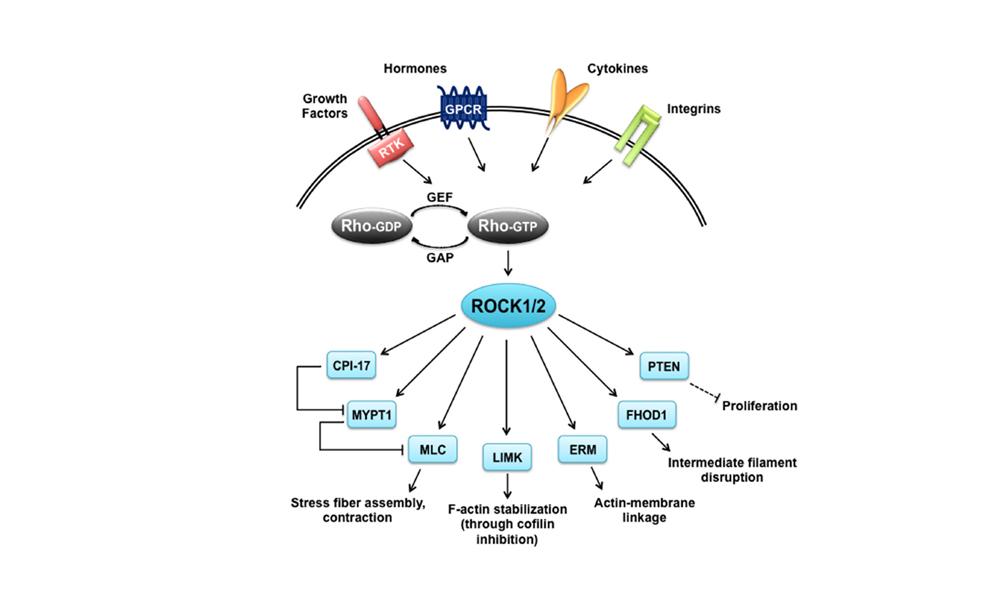
- Source:
- Hartmann S. et al., The Function of Rho-Associated Kinases ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 6:276.
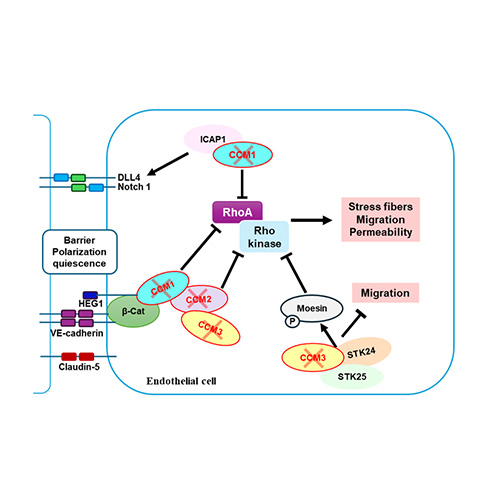
- Source:
- Adopted from Fischer et al., Cerebral cavernous malformations: from CCM genes to endothelial cell homeostasis, Trends Mol Med., 2013; 19(5): 302-308
The ROCK2 inhibitor has been independently developed by Genosco and has generated candidates that selectively inhibit ROCK2 kinase. Research has revealed that the signal transduction processes activated by ROCK are involved in various signaling processes, such as cell proliferation, prevention of apoptosis, cell migration, and secretion of cytokines and chemokines, and according to recent reports, it is also involved in inflammation and fibrosis. Therefore, ROCK2 is a substance that is getting attention as a new treatment target.
Genosco’s ROCK2 candidates are highly potent compared to published inhibitors and possess exceptionally high selectivity, mitigating the toxicity inherent to many pan-ROCK inhibitors developed to date. Furthermore, Genosco’s ROCK2 candidates have exhibited excellent pharmacological efficacy (Ashcroft score) in an animal model of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and superior inhibition on the expression of αSMA, a representative marker of IPF, compared to the competing drug Nintedanib.
-
02.Current Progress
The ROCK2 program has completed preclinical studies and is currently preparing for a Phase 1 clinical trial. Our ROCK2 candidate targeting cerebral cavernous malformations is in the discovery stage.
-
03.About the Disease
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a type of chronic interstitial lung disease (ILDs), and refers not to any one disease, but to all diseases that mainly cause problems with interstices in the lung. The exact cause of the onset of IPF is still unknown.
When tissues between alveoli are damaged, the inflammatory cells penetrate the area repeatedly and the inflammatory state persists, which leads to fibrosis that hardens the lungs. Subsequently, severe structural changes occur in the lung tissues and the lung function gradually decreases, causing death. So far, there are no drugs that have been proven effective for the treatment of IPF. Anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators have been widely used for the treatment of IPF, but their effectiveness has not been proven. IPF is a rare refractory disease, for which a few drugs have been approved by the US FDA, but these drugs have only limited effects of delaying the decline of the lung function without stopping the disease itself.Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM) is a vascular disorder of the brain characterized by clusters of abnormally formed blood vessels that can leak or bleed, causing neurological issues. CCM can occur sporadically or be inherited in a familial form caused by mutations in at least 1 of the 3 CCM genes. The loss of these genes activates the RhoA/ROCK pathway, with ROCK2-- the predominant isoform in the brain—playing a crucial role in regulating endothelial barrier integrity and vascular remodeling. This mechanism drives the development of cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) lesions.
However, clinical advancements in ROCK2-targeted therapies have been limited, primarily due to challenges in crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the difficulty of selectively inhibiting ROCK2 without affecting ROCK1, whose inhibition can result in undesirable side effects. Currently, Genosco is engaged in the development of selective ROCK2 inhibitor for the CCM pathogenesis.
Currently, Genosco is engaged in the rapid development of an orphan drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and is also considering the expansion of indications for cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) through the development of selective ROCK2 inhibitors.